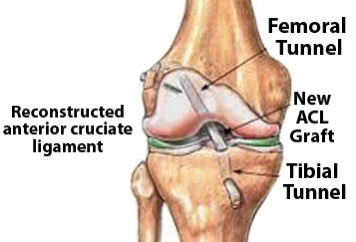
There are roughly 200,000 reported anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) injuries every year. Approximately 65% of reported injuries are surgically reconstructed. More specifically, the reconstructive surgery is known as a graft; a procedure that harvests healthy tissue and transplants it to the traumatized area. The ACL stabilizes the femur on the tibia from movement forwards and backwards, as well as restricting over rotation of the bones when the foot is planted. Reconstruction of the ACL involves the creation of two tunnels, one on the femur (thigh bone) and one on the tibia (shin bone).
The two major types of grafts for ACL injuries are autograft (your tissue) and allograft (cadaver tissue). Each type of graft has pros and cons. The type of graft used depends on a variety of factors; including but not limited to age and physical activity level. For example, a 17 year-old female varsity soccer player would get a different graft than a 38 year-old sedentary male.
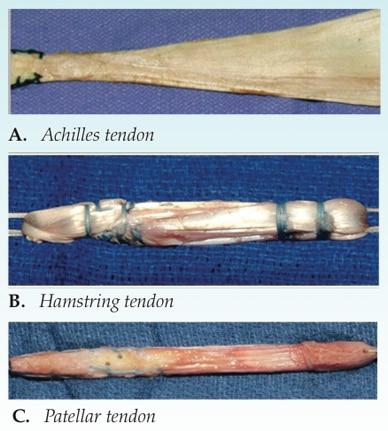
Autografts are harvested from your own tissue. The most common are the quadriceps tendon, patellar tendon and inner hamstring (semitendinosus) tendon.
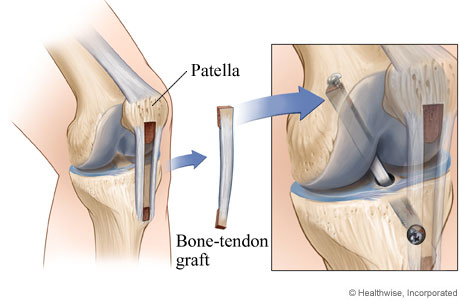
More specifically, patellar tendon grafts are considered the gold standard as they harvest a piece of bone from the inferior pole (bottom) of the patella, a portion of the patellar tendon, a piece of bone from the tibial tuberosity (the bump on the shin). This is called a bone-tendon-bone (BTB) graft, and they help secure the bone tunnelling when they affix the reconstructed ACL in the femur and tibia bones within the joint. Used in young, athletic patients, BTB grafts promote early bone to bone healing around 6 weeks. It is common for patients with BTB grafts to experience quadriceps weakness, anterior knee pain/numbness with kneeling, as well as a higher probability to develop patellar tendonitis following the ACL reconstruction.
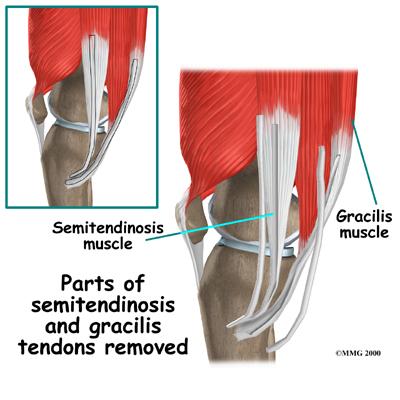
Next, hamstring tendon grafts are harvested from the semitendinosus muscle, where it is double or quadruple wrapped to be inserted into the ACL graft. Benefits of this surgery include a smaller incision in the back of the leg, less anterior knee pain, and greater integrity of the extensor mechanism as they dont impact the quadricep/patellar tendon, good tensile strength, lower incidence of reinjury, return to pre-operative condition. On the other hand, this particular graft yields a longer recovery time, potential damage of the saphenous nerve resulting in medial leg numbness, weakness in hamstring muscle from harvesting, longer time for graft integration (due to absence of bone plugs) as soft tissue healing to bone 8-12 weeks.
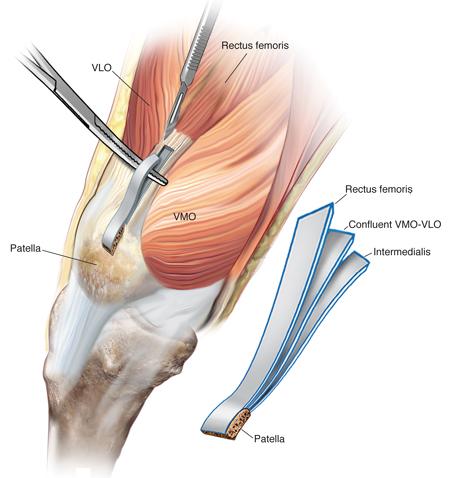
Quadriceps tendon harvesting is less common but becoming a very great option for their strength and resilience. Studies show that the quadriceps tendon has 20% more collagen fibrils per cross-sectional area than the patellar tendon. They can be used in adolescents with open growth plate as it would not violate the tibial tubercle apophysis. Benefits to use of this option include minimal acute postoperative pain, less kneeling pain following surgery, less graft site pain, and less of an effect on strength loss. The biggest flaw would include longer soft tissue healing and recovery time post operatively, and lack of long term follow up studies as it is a relatively new option.
Lastly, allografts are harvested from donor cadaver tissues and include ACL, hamstring, and patellar tendons as options. These are an excellent choice for people who need to return to work faster and don’t necessarily need higher level physical function like running, jumping and cutting. Some benefits include decreased muscle weakness, kneeling pain, risk of patellar fracture, and smaller incision sites. Significant disadvantages of allograft tissue are higher failure rates, increased time to incorporation, variability in mechanical strength due to secondary sterilization techniques, risk of disease transmission, immunogenic reaction, lack of long-term outcome data (especially for young patients under the age of 25), and higher cost.
In closing,
- There is an option for everyone
- Picking the right graft depends on activity level and age.
- Quadriceps tendon autograft has becoming more popular with surgeons and has a lower failure rate in young adults
- Allografts are a great option for those who need to return to usual function at a quicker time

Comments
http://stemcellhelpautism.com/
By Doyle
Comparativo Fortune – jogue a demo . Ganhe com multiplicadores em cassinos como MegaPari. Escolha agora ! Fortune Rabbit cassino Wheel games requires tactics and fortune. Practice wise wagers for a better result. #RouletteTips teste sem arriscar Blackjack needs talent and tactics. Learn the fundamentals and manage your money wisely. #GambleSmart sem baixar
By Meri
Fortune Dragon ou Fortune Ox? – divirta-se sem riscos. Ox com ação rápida em cassinos como 1Win . Teste agora ! Fortune Ox Windows Apostas seguras é essencial. Defina limites de tempo e dinheiro. experiência divertida The rush of placing a big bet is exhilarating, but can also be dangerous. Fortune Ox iOS
By Arnold
mostbet hungary
By Virgie
Slot Fortune Dragon Demo é uma ótima escolha . Explore o tema asiático em cassinos como 1Win . Descubra o dragão! fortune dragon
By Noe
Tigrinho: O Jogo do Brasil – ganhe com bônus! RTP de até 97% em cassinos como Blaze. Ganhe jackpots! Cassinos com Tigrinho Cash out your winnings quickly. Some casinos delay payouts, so check reviews before depositing. 3 bobinas
By Willard
Slots da PG Soft – divirta-se sem riscos. Dragon com tema místico em cassinos como 1Win . Escolha seu slot ! jogo do boi com emoção Bônus aumentam seu saldo, mas leia os termos. Os requisitos de aposta podem ser altos. cassinos online Brasil Slots são os mais fássiveis de jogar. Basta girar e torcer pela sorte! Fortune Ox vale a pena
By August
Mostbet Portugal – opção confiável para apostas . Oferece jogos de alta qualidade . Mostbet Portugal (Adan)
By Angeline
Hyödynnä bonukset – houkuttelevat tarjoukset odottavat. Mostbet Finland
By Willis
Mostbet HU Bónusz
By Reda
Hello! For you I'm Saifullah. Have a look at my site: seo for personal injury lawyer
By Saifullah
Ensured security and legality of gaming in India Pin-Up Casino operates under a Curacao license and complies with all safety regulations to ensure your data and transactions stay safe. Play worry-free and enjoy top-quality services. pin up casino Is Pin-Up Casino Truly the Best for Indian Players? If you’re an gambler from India, you may have heard about Pin Up casino, but is it genuinely the top option? With a massive sign-up bonus, a variety of games, and the ability to deposit using INR, it seems like a excellent option. But what do you think? Is Pin-Up Casino really living up to its claims in India?
By Dan
Join Now with Bet9ja's Simple Mobile Version! old mobile bet9ja com Looking for a familiar betting interface? Bet9ja's Old Mobile version offers users a fast way to place bets, with no complicated features. Access all betting options, from soccer to casino games, and take advantage of exclusive promotions. old bet9ja
By Don
Play comfortably anytime with the Taya365 app taya365 app Step into a rewarding gaming experience at Taya365! Play your favorite casino games and take home big prizes with every spin, bet, and win. Ready to win? taya365 app casino
By Booker
Wow, what a immense read! I absolutely enjoyed how you approached this subject-matter — it's indubitably something I haven’t consideration about in that modus operandi before. Your insights were wonderful inviting, and I relish how you made entire lot so relatable. I can’t interval to go steady with more posts like this! Take care up the wondrous post! gay porno
By Fermin
Wow, what a large understand! I in the end enjoyed how you approached this matter — it's assuredly something I haven’t musing about in that sense before. Your insights were super inviting, and I angel how you made entire lot so relatable. I can’t hold on to charge of more posts like this! Keep up the fearful post! gayporno
By Grazyna
https://mcpipokinha23.shop This paragraph offers clear idea in support of the new viewers of blogging, that truly how to do blogging.
By Marietta
The 10 Most Terrifying Things About Ticktok Pornstars Ticktok pornstars
By Kirby
https://mobilecoin.chat/ ATGepower
By Leigh
https://Dianoetic.net/ ATGepower
By Steve
https://barcampusa.com/ ATGepower Aiko’s work goes beyond blogging. She regularly collaborates with renewable energy companies, offering her insights to help develop more efficient solar technologies. She also speaks at international conferences, advocating for the widespread adoption of solar power.
By Raleigh
Best Newcomer Pornstar Tools To Make Your Daily Life Best Newcomer Pornstar Technique Every Person Needs To Be Able To best newcomer Pornstar
By Jannette